|
|
|---|
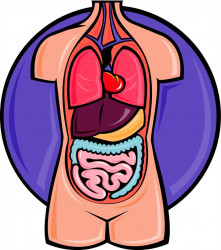
| a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function |
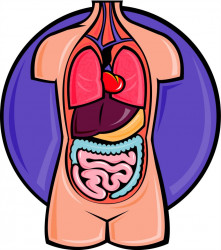
| a muscular organ that pumps blood through the body, traditionally thought to be the seat of emotion |
| the control centre of the central nervous system of a person or an animal located in the skull which is responsible for perception, cognition, attention, memory, emotion, and action |
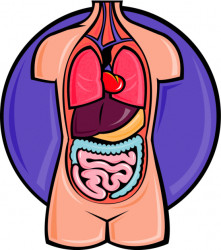
| a biological organ that extracts oxygen from the air |
| a large organ in the body that stores and metabolizes nutrients, destroys toxins and produces bile, responsible for thousands of biochemical reactions |
| an organ which serves the body as a natural filter of the blood, and removes wastes which are diverted to the urinary bladder |
| the movement of the blood in the blood-vascular system, by which it is brought into close relations with almost every living elementary constituent |
| a vital liquid flowing in the body that usually conveys nutrients and oxygen, it is coloured red by hemoglobin and is conveyed by arteries and veins |
| the segment of the alimentary canal extending from the stomach to the anus and, in humans and other mammals, consists of two segments, the small intestine and the large intestine |
| a blood vessel that transports blood from the capillaries back to the heart |
| an efferent blood vessel from the heart, conveying blood away from the heart regardless of oxygenation status |
| an organ composed of muscle tissue, producing force and causing motion |
-
organ, organs['ɔːɹ.gɘn](noun)
-
- a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function
-
- The heart is an important organ.
imgserver-62-2475189+1
-
heart, hearts[hɑːt](noun)
-
- a muscular organ that pumps blood through the body, traditionally thought to be the seat of emotion
-
- In the lightness of my heart I sang catches of songs.
imgserver-62-4638681
-
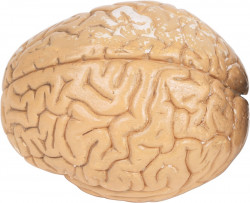
brain, brains[bɹeɪn](noun)
-
- the control centre of the central nervous system of a person or an animal located in the skull which is responsible for perception, cognition, attention, memory, emotion, and action
-
- The brain controls the other organ systems of the body.
imgserver-62-2475189+2
-
-
- a biological organ that extracts oxygen from the air
-
- The human lungs flank the heart and great vessels in the chest cavity.
imgserver-62-88353928
-
liver, livers[lɪvə(r)](noun)
-
- a large organ in the body that stores and metabolizes nutrients, destroys toxins and produces bile, responsible for thousands of biochemical reactions
-
- The liver is necessary for survival.
-
kidney, kidneys[ˈkɪdni](noun)
-
- an organ which serves the body as a natural filter of the blood, and removes wastes which are diverted to the urinary bladder
-
- The kidneys are paired organs with several functions.
-
circulation, circulations[ˈsɜː(ɹ).kjʊˌleɪ.ʃən](noun)
-
- the movement of the blood in the blood-vascular system, by which it is brought into close relations with almost every living elementary constituent
-
- Something is wrong with my circulation, I fainted yesterday.
imgserver-62-5092838
-
blood[blʌd](uncountable noun)
-
- a vital liquid flowing in the body that usually conveys nutrients and oxygen, it is coloured red by hemoglobin and is conveyed by arteries and veins
-
- When she sees blood, she faints.
imgserver-62-2475189+4
-
bowel, bowels[baʊl](noun)
-
- the segment of the alimentary canal extending from the stomach to the anus and, in humans and other mammals, consists of two segments, the small intestine and the large intestine
-
- People have different sized bowels according to their size and age.
-
-
- a blood vessel that transports blood from the capillaries back to the heart
-
- Veins differ from arteries in structure and function.
imgserver-62-4652637
-
artery, arteries[ˈɑː.tə.ɹɪ](noun)
-
- an efferent blood vessel from the heart, conveying blood away from the heart regardless of oxygenation status
-
imgserver-62-5087157
-
muscle, muscles[ˈmʌsəl](noun)
-
- an organ composed of muscle tissue, producing force and causing motion
-
- The muscles in his legs strained under the load.
![]()
Ad
Enter the correct word in the text box and then confirm your entry. If you make a mistake, the word will be repeated automatically! Learn with pictures and examples by customizing the vocabulary trainer to fit your needs.
Keyboard shortcuts: Enter: Check / Go to next question | Alt+1: Hint | Alt+2: Solution
Complete the word by entering the missing letters!
| organ |
| heart |
| brain |
| lung |
| liver |
| kidney |
| circulation |
| blood |
| bowel |
| vein |
| artery |
| muscle |
Click on the two cards that belong together!
Word and Image
Tries: 0heart | |
brain | |
bowel | |
lung | |
muscle | |
blood | |
artery | |
liver | |
Word and Definition
Tries: 0heart | a muscular organ that pumps blood through the body, traditionally thought to be the seat of emotion |
liver | a large organ in the body that stores and metabolizes nutrients, destroys toxins and produces bile, responsible for thousands of biochemical reactions |
kidney | an organ which serves the body as a natural filter of the blood, and removes wastes which are diverted to the urinary bladder |
artery | an efferent blood vessel from the heart, conveying blood away from the heart regardless of oxygenation status |
circulation | the movement of the blood in the blood-vascular system, by which it is brought into close relations with almost every living elementary constituent |
vein | a blood vessel that transports blood from the capillaries back to the heart |
blood | a vital liquid flowing in the body that usually conveys nutrients and oxygen, it is coloured red by hemoglobin and is conveyed by arteries and veins |
lung | a biological organ that extracts oxygen from the air |
organ | a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function |
bowel | the segment of the alimentary canal extending from the stomach to the anus and, in humans and other mammals, consists of two segments, the small intestine and the large intestine |
brain | the control centre of the central nervous system of a person or an animal located in the skull which is responsible for perception, cognition, attention, memory, emotion, and action |
muscle | an organ composed of muscle tissue, producing force and causing motion |
Definition and Image
Tries: 0 | a muscular organ that pumps blood through the body, traditionally thought to be the seat of emotion |
| a large organ in the body that stores and metabolizes nutrients, destroys toxins and produces bile, responsible for thousands of biochemical reactions |
| the segment of the alimentary canal extending from the stomach to the anus and, in humans and other mammals, consists of two segments, the small intestine and the large intestine |
| an efferent blood vessel from the heart, conveying blood away from the heart regardless of oxygenation status |
| a vital liquid flowing in the body that usually conveys nutrients and oxygen, it is coloured red by hemoglobin and is conveyed by arteries and veins |
| a biological organ that extracts oxygen from the air |
| an organ composed of muscle tissue, producing force and causing motion |
| the control centre of the central nervous system of a person or an animal located in the skull which is responsible for perception, cognition, attention, memory, emotion, and action |